Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Error Propagation in Geological Models¶
This example demonstrates uncertainty quantification through error propagation. We perturb a surface point’s Z-coordinate and propagate the uncertainty through the model.
Import Libraries¶
import numpy as np
import gempy as gp
import gempy_viewer as gpv
import gempy_probability as gpp
import torch
import pyro
import pyro.distributions as dist
from pyro.distributions import Distribution
import arviz as az
from gempy_engine.core.backend_tensor import BackendTensor
from gempy_engine.core.data.interpolation_input import InterpolationInput
from gempy_probability.modules.plot.plot_gempy import plot_gempy
# Set random seeds for reproducibility
seed = 4003
pyro.set_rng_seed(seed)
torch.manual_seed(seed)
np.random.seed(1234)
Import paths configuration
from mineye.config import paths
Define Model Extent and Resolution¶
min_x = -707521
max_x = -675558
min_y = 4526832
max_y = 4551949
max_z = 505
model_depth = -500
extent = [min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y, model_depth, max_z]
# Model resolution: use octree with refinement level 5
resolution = None
refinement = 5
Get Data Paths¶
mod_or_path = paths.get_orientations_path()
mod_pts_path = paths.get_points_path()
print(f"Orientations: {mod_or_path}")
print(f"Points: {mod_pts_path}")
Orientations: /home/leguark/PycharmProjects/Mineye-Terranigma/examples/Data/Model_Input_Data/Simple-Models/orientations_mod.csv
Points: /home/leguark/PycharmProjects/Mineye-Terranigma/examples/Data/Model_Input_Data/Simple-Models/points_mod.csv
Create GemPy Geological Model¶
geo_model = gp.create_geomodel(
project_name='error_propagation_model',
extent=extent,
refinement=refinement,
resolution=resolution,
importer_helper=gp.data.ImporterHelper(
path_to_orientations=mod_or_path,
path_to_surface_points=mod_pts_path,
)
)
Map Geological Units¶
gp.map_stack_to_surfaces(
gempy_model=geo_model,
mapping_object={
"Tournaisian_Plutonites": ["Tournaisian Plutonites"],
}
)
Switch to PyTorch Backend¶
Required for probabilistic modeling
BackendTensor.change_backend_gempy(engine_backend=gp.data.AvailableBackends.PYTORCH)
print("✓ Switched to PyTorch backend")
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
✓ Switched to PyTorch backend
Define Prior Distribution¶
Prior Predictive Sampling vs. Posterior Sampling
Prior Predictive Sampling: Generating data from the model using parameters drawn from the prior distribution. It answers: “What kind of models/data do our initial beliefs produce?” It’s a way to check if the model and priors are reasonable before considering observations.
Posterior Sampling: Generating parameters that are consistent with both our initial beliefs (priors) AND the observed data. It answers: “What parameters are most likely given the data we’ve seen?”
In this example, we focus on Prior Predictive Sampling to see how uncertainty in input coordinates propagates to the final structural geometry.
We’ll add uncertainty to the Z-coordinate of the first surface point.
from mineye.config.example_parameters import TharsisModelConfig
FORMATION_COLORS = TharsisModelConfig.TharsisDataProcessingConfig.FORMATION_COLORS
def modify_z_for_surface_point1(
samples: dict[str, Distribution],
geo_model: gp.data.GeoModel,
) -> InterpolationInput:
"""Modify the Z-coordinate of the first surface point based on samples."""
prior_key = r'$\mu_{top}$'
from gempy.modules.data_manipulation import interpolation_input_from_structural_frame
interp_input = interpolation_input_from_structural_frame(geo_model)
new_tensor: torch.Tensor = torch.index_put(
input=interp_input.surface_points.sp_coords,
indices=(torch.tensor([0]), torch.tensor([2])),
values=(samples[prior_key])
)
interp_input.surface_points.sp_coords = new_tensor
return interp_input
Set Prior Parameters¶
Normal distribution around the original point location
original_z = geo_model.surface_points_copy_transformed.xyz[0, 2]
print(f"Original Z-coordinate: {original_z:.2f}")
model_priors = {
r'$\mu_{top}$': dist.Normal(
loc=original_z,
scale=torch.tensor(0.002, dtype=torch.float64)
)
}
print(f"Prior: Normal(loc={original_z:.2f}, scale=0.001)")
Original Z-coordinate: 0.00
Prior: Normal(loc=0.00, scale=0.001)
Create Probabilistic Model¶
prob_model: gpp.GemPyPyroModel = gpp.make_gempy_pyro_model(
priors=model_priors,
set_interp_input_fn=modify_z_for_surface_point1,
likelihood_fn=None,
obs_name=None
)
print("✓ Probabilistic model created")
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
✓ Probabilistic model created
Run Prior Predictive Sampling¶
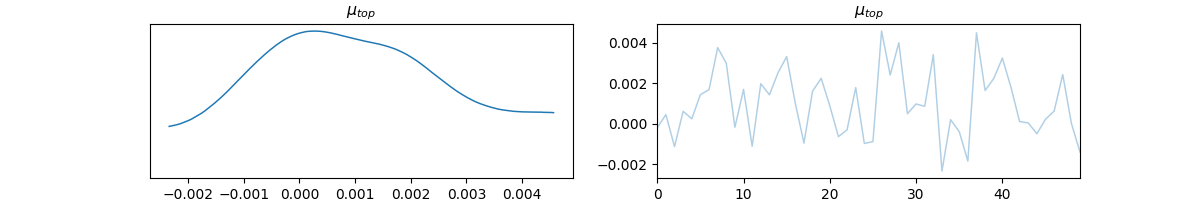
Sample from the prior distribution and propagate through the model
n_samples = 50
print(f"Running {n_samples} prior predictive samples...")
prior_inference_data: az.InferenceData = gpp.run_predictive(
prob_model=prob_model,
geo_model=geo_model,
y_obs_list=[],
n_samples=n_samples,
plot_trace=True
)
print("✓ Prior predictive sampling complete")
Running 50 prior predictive samples...
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
✓ Prior predictive sampling complete
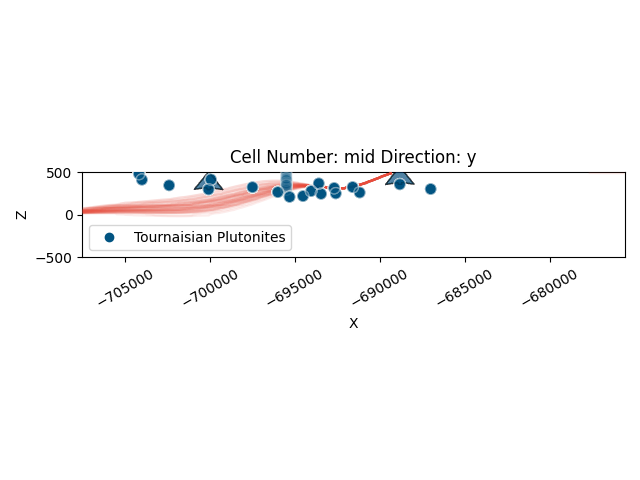
Visualize Uncertainty¶
Plot the model with sampled surface points
def update_model_for_plotting(geo_model: gp.data.GeoModel, sample_value: float, sample_idx: int):
"""Update model with a sampled Z-coordinate value."""
xyz = np.zeros((1, 3))
xyz[0, 2] = sample_value
world_coord = geo_model.input_transform.apply_inverse(xyz)
# Modify the surface point
gp.modify_surface_points(
geo_model=geo_model,
slice=0,
Z=world_coord[0, 2]
)
# Create base plot
p2d = gpv.plot_2d(
model=geo_model,
show_topography=False,
legend=False,
show_lith=False,
show_data=False,
show=False,
ve=5
)
# Overlay sampled models
plot_gempy(
geo_model=geo_model,
n_samples=50,
samples=(prior_inference_data.prior[r'$\mu_{top}$'].values[0, :]),
update_model_fn=update_model_for_plotting,
gempy_plot=p2d,
contour_colors=[FORMATION_COLORS['Tournaisian Plutonites']]
)
print("✓ Visualization complete")
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
/home/leguark/PycharmProjects/gempy_viewer/gempy_viewer/modules/plot_2d/drawer_contours_2d.py:38: UserWarning: The following kwargs were not used by contour: 'linewidth', 'contour_colors'
contour_set = ax.contour(
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Using sequential processing for 1 surfaces
✓ Visualization complete
Summary Statistics¶
samples = prior_inference_data.prior[r'$\mu_{top}$'].values[0, :]
print(f"\nSampled Z-coordinate statistics:")
print(f" Mean: {samples.mean():.4f}")
print(f" Std: {samples.std():.4f}")
print(f" Min: {samples.min():.4f}")
print(f" Max: {samples.max():.4f}")
print(f" Original: {original_z:.4f}")
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
Sampled Z-coordinate statistics:
Mean: 0.0010
Std: 0.0017
Min: -0.0023
Max: 0.0046
Original: 0.0004
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 0.859 seconds)
